Industries
Get direct access to our extensive portfolio of optical products and specialist technical expertise.
Get direct access to our extensive portfolio of optical products and specialist technical expertise.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of telecommunications, the single mode fiber transceiver has emerged as a pivotal component in enhancing data transmission efficiency. Renowned expert Dr. Emily Carter, a leading figure in optical communication technologies, once stated, "The single mode fiber transceiver is instrumental in achieving higher bandwidths over longer distances, making it essential for modern networks." This assertion underscores the device's role in facilitating clearer, faster, and more reliable communication channels.
Single mode fiber transceivers operate using a single strand of glass fiber, allowing them to transmit data over significant distances with minimal signal loss. As the demand for high-speed internet and seamless connectivity continues to rise, understanding the mechanics and advantages of single mode fiber transceivers becomes increasingly crucial. They are designed to support cutting-edge applications, from enterprise-level networking to expansive telecommunications infrastructures, revolutionizing how data is exchanged across the globe.
In this context, exploring the fundamental principles behind single mode fiber transceivers and their practical applications will provide valuable insights into their importance in the current and future landscape of digital communication. The synergy of innovation and engineering represented by these devices highlights their vital position in shaping connectivity in an increasingly digital world.

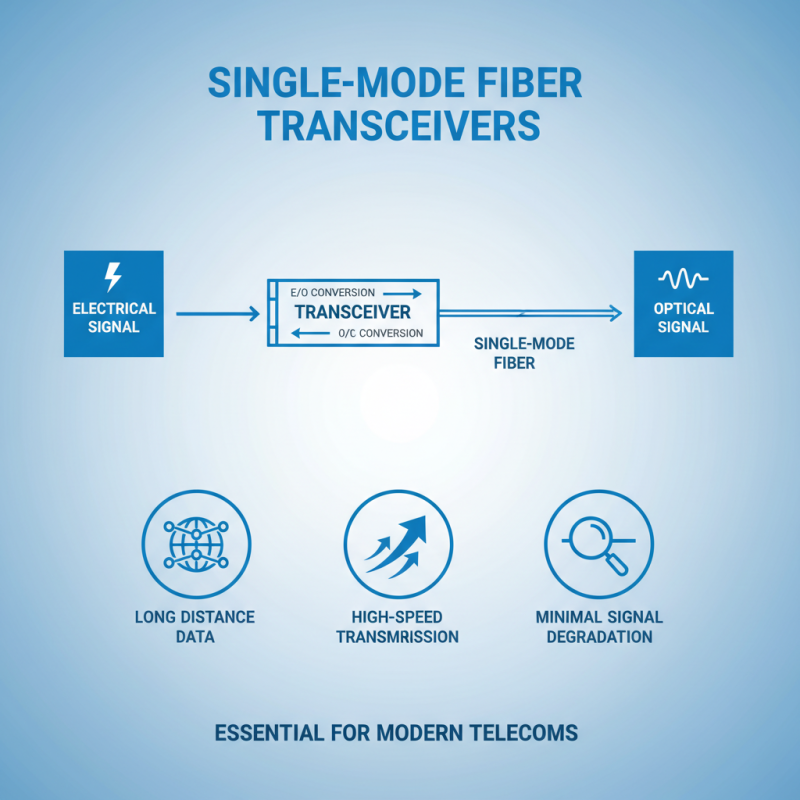
Single mode fiber transceivers play a crucial role in modern telecommunications, providing high-speed data transmission over long distances. Unlike multimode fibers that use multiple light paths, single mode fibers allow only one light path, which minimizes signal degradation and enables faster data rates. The transceiver itself is a vital component that converts electrical signals into optical signals for transmission through the fiber and vice versa. This conversion is essential for ensuring that data can travel efficiently over the fiber infrastructure.
The operation of a single mode fiber transceiver involves the use of laser diodes that emit light at specific wavelengths. The precise alignment of the optical components within the transceiver is critical, as even the slightest misalignment can lead to significant loss of signal strength. These transceivers can support various protocols and are designed to work over vast distances, making them ideal for applications in telecommunications networks, data centers, and enterprise networks. Their high bandwidth capabilities and low latency make single mode fiber transceivers an important asset for any organization looking to enhance its data transmission capabilities.
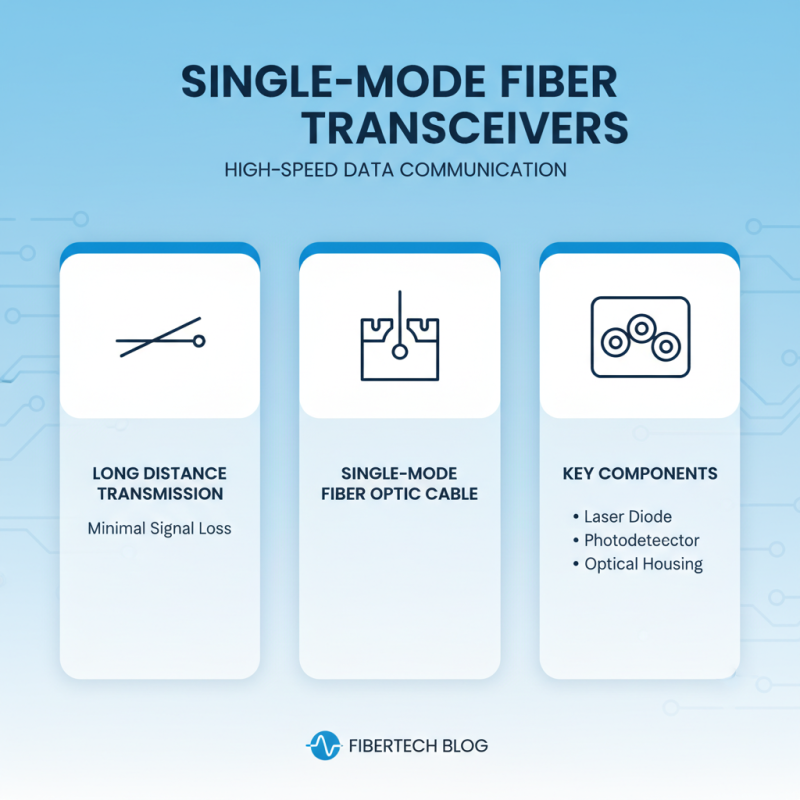
Single mode fiber transceivers play a vital role in high-speed data communication networks. These transceivers are designed to transmit data over long distances with minimal signal loss, utilizing a single mode fiber optic cable. Key components of a single mode fiber transceiver include the laser diode, photodetector, and the optical housing.
The laser diode is responsible for generating the light signal that travels through the fiber. It operates at specific wavelengths, typically around 1310 nm or 1550 nm, chosen for optimal transmission performance. According to the Fiber Optic Association, single mode fiber offers significantly reduced attenuation compared to multimode fiber, with typical loss rates around 0.2 dB/km at 1550 nm. This makes it ideal for long-distance communication, where data integrity and speed are crucial.
Another critical component is the photodetector, which converts the received light signal back into an electrical signal. This component must be highly sensitive to ensure that it can detect the weak signals that may have been attenuated over long distances. Additionally, the optical housing maintains the alignment and protection of these sensitive components, ensuring reliable operation under various environmental conditions. Reports indicate that the demand for single mode fiber transceivers is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 10% through 2025, driven by the increasing need for high-bandwidth applications and long-distance communications.
Single mode fiber transceivers play a critical role in modern data transmission, especially in long-distance communication networks. Utilizing a single solid core, typically with a diameter of 8 to 10 microns, these transceivers allow light to travel directly down the fiber, resulting in minimal signal loss and allowing for greater transmission distances compared to multimode fibers. According to a report by Markets and Markets, the global fiber optics market is expected to reach $10.90 billion by 2026, highlighting the growing importance of efficient data transmission solutions like single mode fiber transceivers in both commercial and residential settings.
The functionality of single mode fiber transceivers hinges on their ability to convert electrical signals into optical signals, and vice versa, facilitating high-speed data transfer across vast distances. The use of lasers as light sources, particularly distributed feedback lasers (DFB), ensures that the light transmitted is coherent, allowing for data rates that can exceed 100 Gbps. A study published by the Fiber Optic Association noted that organizations implementing single mode fiber can achieve transmission distances up to 100 kilometers without significant degradation, making it an ideal choice for telecommunications, cable television, and internet service providers looking to optimize their networks. This efficiency highlights why single mode fiber transceivers are increasingly being integrated into infrastructure upgrades as data demands continue to rise.
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission Distance | Up to 40 kilometers or more | Long-distance communication with minimal signal loss |
| Core Diameter | Typically 9 micrometers | Supports higher bandwidth and reduces modal dispersion |
| Light Source | Laser (typically DFB or VCSEL) | Provides coherent light for efficient transmission |
| Connector Types | LC, SC, MPO/MTP | Flexible connectivity options for various installations |
| Data Rate | From 1 Gbps to 400 Gbps and beyond | High-speed data transmission suitable for modern networks |
| Wavelengths | Common wavelengths 1310 nm and 1550 nm | Optimized for minimal attenuation over long distances |
| Form Factor | SFP, SFP+, XFP, QSFP+ | Compact design fits various networking equipment |
Single mode fiber transceivers offer a range of advantages that make them ideal for high-speed, long-distance communication. One of the most significant benefits is their ability to transmit data over vast distances—up to 100 kilometers or more—without significant signal degradation. This is largely due to the single mode fiber's small core diameter, which allows light to travel in a straight path, reducing modal dispersion. Additionally, they tend to have lower attenuation compared to multimode fibers, resulting in clearer signals and higher bandwidth capabilities, making them suitable for applications such as telecommunications and data centers.
However, single mode fiber transceivers also come with some disadvantages. The initial cost can be higher than that of multimode solutions, primarily due to the sophisticated technology involved in their design and manufacture. Moreover, the installation and testing processes can be more complex, requiring specialized skills and equipment to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, while single mode fibers excel in long-distance transmission, they may not be the best choice for short-range applications, where multimode fibers can provide sufficient bandwidth at a lower cost. Balancing these advantages and disadvantages is crucial for organizations when deciding on the appropriate fiber optic technology for their networking needs.
Single Mode Fiber Transceivers are crucial components in high-speed networking systems, designed to transmit data over long distances with minimal signal loss. The unique characteristics of single mode fiber, which features a very thin core less than 10 microns in diameter, enable these transceivers to support the transmission of light signals in a single mode, resulting in low attenuation and high bandwidth. According to the market research conducted by Allied Market Research, the global single mode fiber market is projected to reach $9.5 billion by 2025, highlighting their growing significance in modern communication infrastructures.
In networking systems, single mode fiber transceivers are widely employed in applications such as long-haul telecommunications, data center interconnections, and enterprise networks. Their ability to maintain high data rates over distances exceeding 40 kilometers makes them ideal for connecting remote sites and enhancing connectivity within large organizations. Industry data from Research and Markets indicates that the demand for single mode fiber transceivers in the data center sector alone is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.2% from 2020 to 2025, driven by the increasing needs for data processing and storage capabilities. This trend underscores the integral role single mode transceivers play in supporting the ever-expanding networking requirements of the digital age.





