Industries
Get direct access to our extensive portfolio of optical products and specialist technical expertise.
Get direct access to our extensive portfolio of optical products and specialist technical expertise.
In today's digital age, the importance of optical cables cannot be overstated. These cables are essential for high-speed data transmission, transforming the way we connect. According to Dr. Emily Chen, an expert in optical communications, "Optical cables are the backbone of modern networking." Her words highlight the critical role these cables play.
Yet, many users remain unaware of the intricacies of optical cables. There are numerous factors to consider when using them. For example, the differences between single-mode and multi-mode cables can be confusing. This confusion can lead to suboptimal choices, impacting performance. Often, users overlook essential details like cable length and transceiver compatibility.
While optical cables hold great promise, they are not without pitfalls. Misunderstanding their specifications can lead to wasted resources. Additionally, installation challenges can arise, especially for those lacking technical expertise. It's crucial to embrace the learning process in this rapidly changing field. Understanding optical cables better can make a significant difference in both personal and professional settings.

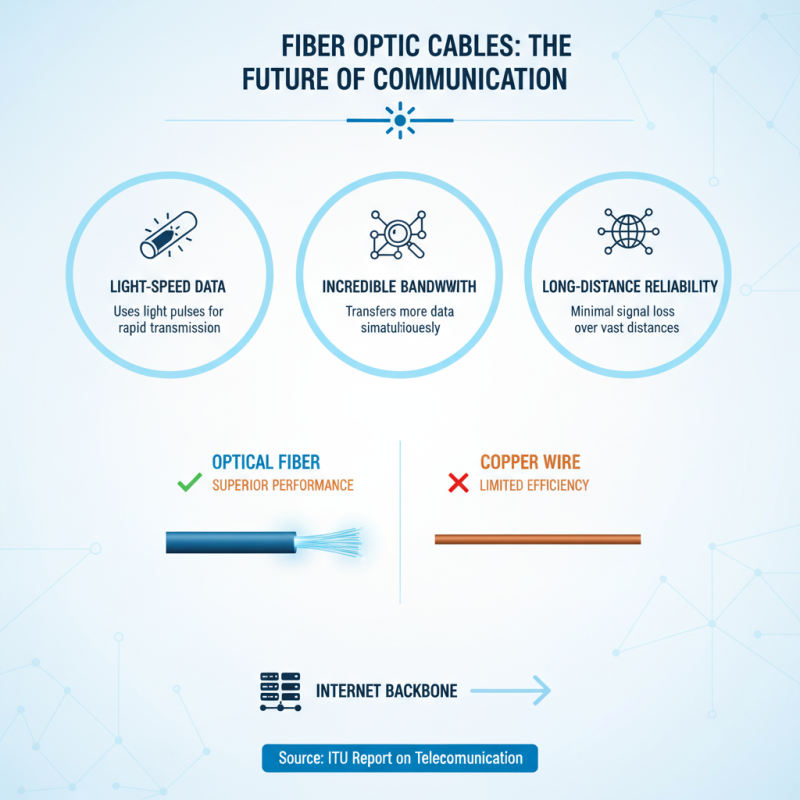
Optical cables are integral to modern communication. They use light to transmit data, enabling faster speeds and greater bandwidth. Fiber optics outperform traditional copper wires in data transfer efficiency. According to a report by the International Telecommunication Union, optical fiber can transmit information over long distances with minimal signal loss. This capability makes it essential for internet backbone connections.
The basic working principle involves total internal reflection. Light signals travel through a glass or plastic core surrounded by a cladding layer with a lower refractive index. This structure keeps the light contained, allowing data to be sent rapidly. A recent industry survey noted that optical fiber can carry data rates exceeding 1 Gbps over distances of more than 100 kilometers without amplification.
Despite these advantages, there are challenges. Installing optical cables can be costly and complex. They are also more fragile than copper cables. Handling requires care to avoid damaging the fibers. Maintenance can be more difficult, too. Ensuring that all connections are intact is crucial for performance. As demand for high-speed internet continues to grow, these factors must be considered.
Optical cables offer several advantages over traditional copper cables. One major benefit is their ability to transmit data at much higher speeds. This is crucial for modern applications like streaming and gaming. With fiber optics, you can experience faster uploads and downloads. The data travels as light, so there are fewer delays.
Another key point is distance. Optical cables can carry signals over much longer distances without losing signal quality. This makes them ideal for large networks and data centers. In contrast, copper cables often experience degradation over shorter lengths. The flexibility of optical cables also allows for easier installation in tight spaces.
However, there are challenges to consider. Optical cables can be more fragile than copper. They require careful handling during setup and use. Additionally, the initial cost can be higher. Not everyone may find the transition easy. But the benefits often outweigh these drawbacks for many applications. Understanding both sides is important for making the right choice.
| Benefit | Description | Comparison with Copper Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Higher Bandwidth | Optical cables can support higher data rates. | Copper cables are limited in the amount of data they can transmit. |
| Longer Distance | Optical cables can transmit data over much longer distances without loss. | Copper cables require repeaters for long distances. |
| Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference | Optical fibers are not affected by electromagnetic interference. | Copper cables can suffer from interference, leading to signal degradation. |
| Greater Security | Harder to tap into without detection. | Copper cables can be easily tapped. |
| Reduced Weight | Optical cables are lighter than copper cables. | Copper cables are heavier, making installation more challenging. |
| Less Signal Loss | Lower attenuation than copper, resulting in better signal quality. | Copper cables can experience significant signal loss. |
| Resistance to Environmental Factors | Better suited for harsh environments. | Copper can corrode or degrade in certain conditions. |
| Future-Proof Technology | Prepared to handle growing data demands. | Copper becomes obsolete as bandwidth requirements increase. |
| Lower Total Cost of Ownership | While initial costs may be higher, lower maintenance and replacement costs make them cost-effective. | Copper can have higher long-term maintenance costs. |
| Supports Advanced Technologies | Essential for technologies like fiber-optic communication. | Copper lacks the speed and efficiency required for modern applications. |
Optical fiber plays a crucial role in modern telecommunications. It uses light to transmit data, providing higher speeds than traditional cables. Many companies rely on this technology to improve communication.
Hospitals, schools, and businesses often connect using fiber optics. The speed of data transfer is vital for their operations.
In data centers, optical cables connect servers efficiently. They enable rapid data exchange critical for cloud services. Even minor delays can cause issues in high-demand environments. Fiber optics also mitigate interference, creating more reliable connections.
However, installation can be challenging, requiring careful handling and expertise. Many users underestimate this complexity.
Residential internet providers use fiber optics to offer fast connections. It allows streaming, gaming, and browsing without disruptions. Despite its advantages, some areas still lack access to fiber infrastructure. This creates a digital divide that needs attention.
Users must advocate for better services in their regions. The gap remains a challenge for many.
Optical cables play a vital role in modern communication. They come in two main types: single-mode and multi-mode. Understanding these types is key for making informed decisions.
Single-mode fibers have a small core diameter. This allows one light signal to travel through the fiber. They are ideal for long distances. These fibers reduce light loss, but they require precise alignment. However, they can be challenging to install. Many users struggle with setup errors due to this precision.
On the other hand, multi-mode fibers have a larger core. They support multiple light modes, which can make installation easier. This type is often used in data centers or shorter distances. However, their performance degrades over long runs. Users must be aware of the distance limitations when choosing this type. Cost can also be a factor. Sometimes, the cheapest option isn't the best for long-term use.
When selecting optical cables, several factors require attention. First, the length of the cable matters. Longer cables may suffer from signal loss, so matching the cable length to your setup is crucial. A 25-foot cable might work for one room, while a 50-foot will be needed for another. Keep in mind that excess length can lead to clutter.
The type of optical fiber is also significant. Single-mode fibers offer higher performance over long distances. Conversely, multi-mode fibers work well for shorter applications. You should evaluate the environment too. Indoor cables differ from outdoor ones, particularly in terms of durability and weather resistance. It’s essential to reflect on where you will use the cable.
Connector types are another vital element to consider. Different devices require specific connectors. Choosing the wrong type can result in compatibility issues. Think about future upgrades as well. Investing in a more versatile cable might save you money later. Each choice impacts performance, so weigh them carefully.





